Etiology
Susceptible Hosts
Cattle are more susceptible. A wide range of hosts like buffalo, sheep, goat, deer, hadge hog, pig and camel are susceptible to this infection. Dog, cat and man may occasionally be infected.
Mode of Transmission
Spread through direct contact with infected animal, contact with infected material, air ways.
Clinical Symptoms
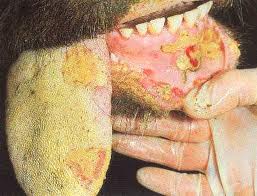
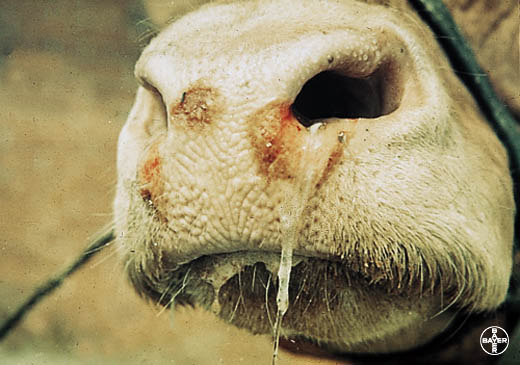
Temp. 104 – 106 F. anorexia, drop in milk yield, followed by appearance of vesicles in oral mucosa, inter digital space, udder, profuse salivation, lameness. Drooling of foamy, ropy salivation and protrusion of tongue. Pregnant animal may abort. Young animals die without exhibiting clinical manifestation.
Control